Dash7 Virtual Meeting September 23th
Agenda:
17.00 Introduction – Maarten Weyn
17.05 Use case; Vestfold Audio AS, Alert system for human wellbeing – Trond Enger
17.25 Q&A on Vestfold use case
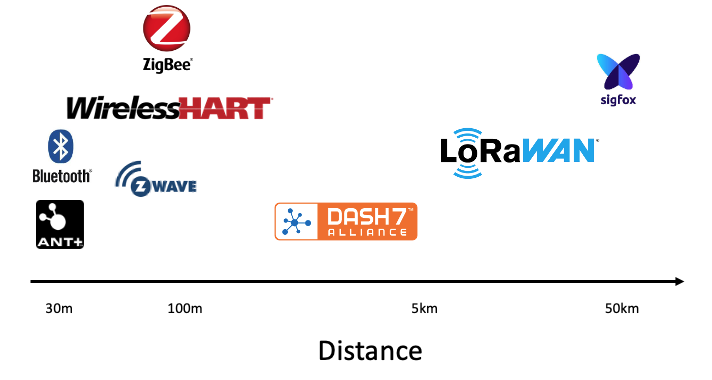
17.35 Why and when to select DASH7, DASH7 top 5 characteristics
Frank Gielissen
17.55 Q&A on Top 5 characteristics
18.05 Q&A on DASH7
18.15 Closing Maarten Weyn
You can rewatch the whole session online: https://www.crowdcast.io/e/dash7-virtual-meeting
Or the individual presentations using the links in the agenda.